Buoy B | Hackaday Dream Team 2020
Buoy B V1.0 is a 102.46 mm x 44.20 mm PCB that integrates 4 of the main components (ESP32, LoRa, GPS and Motor Driver).
Main Components
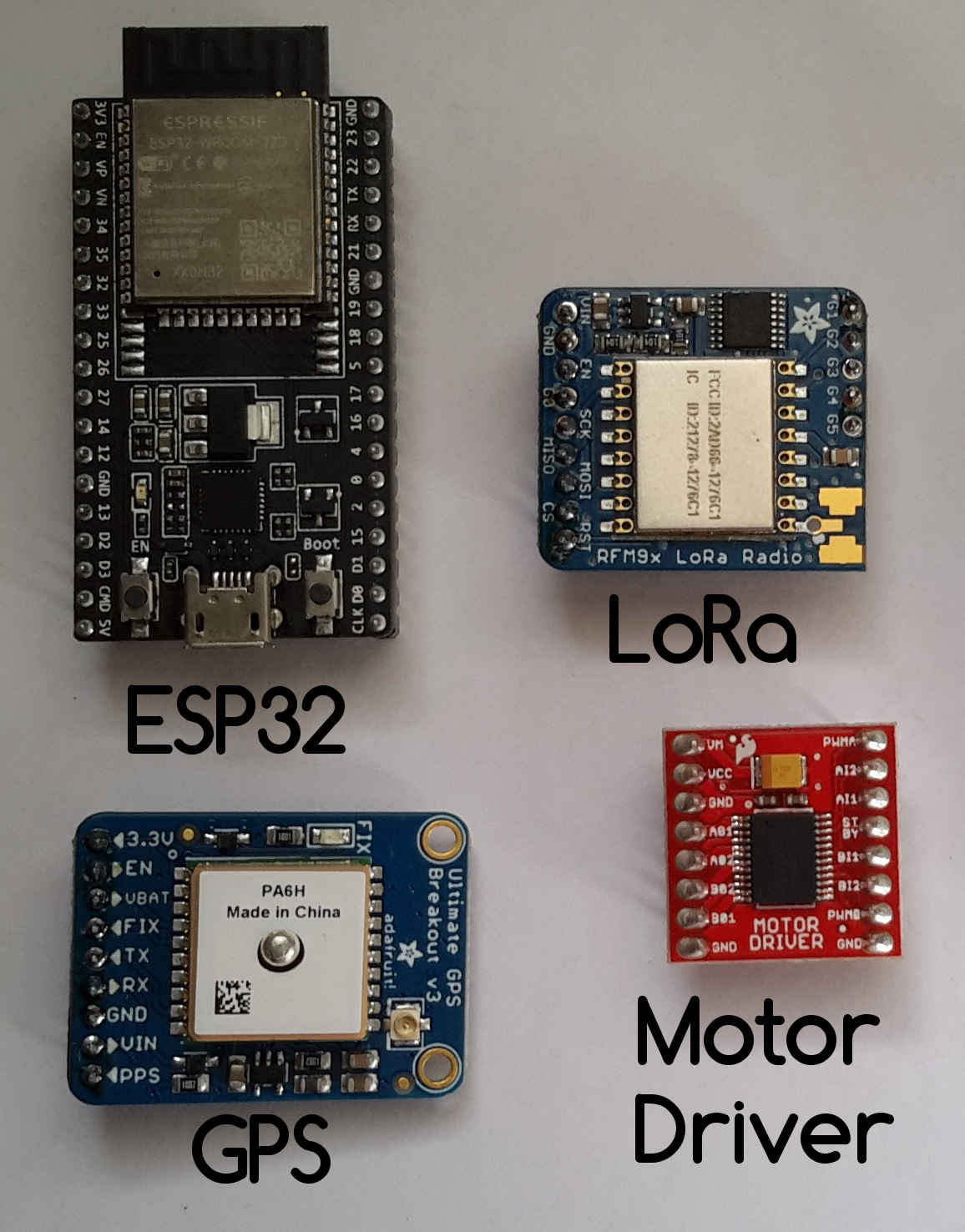
Main components of Buoy B v1.0.
Sources:
- ESP32: ESP32-DEVKITC-32D
- LoRa: RFM95W LoRa Radio
- GPS: Adafruit Ultimate GPS
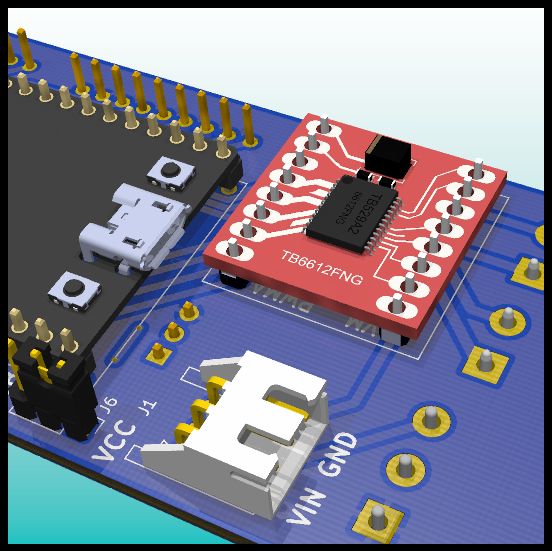
- Motor Driver: TB6612FNG MOTOR DRIVER BOARD
Schematic
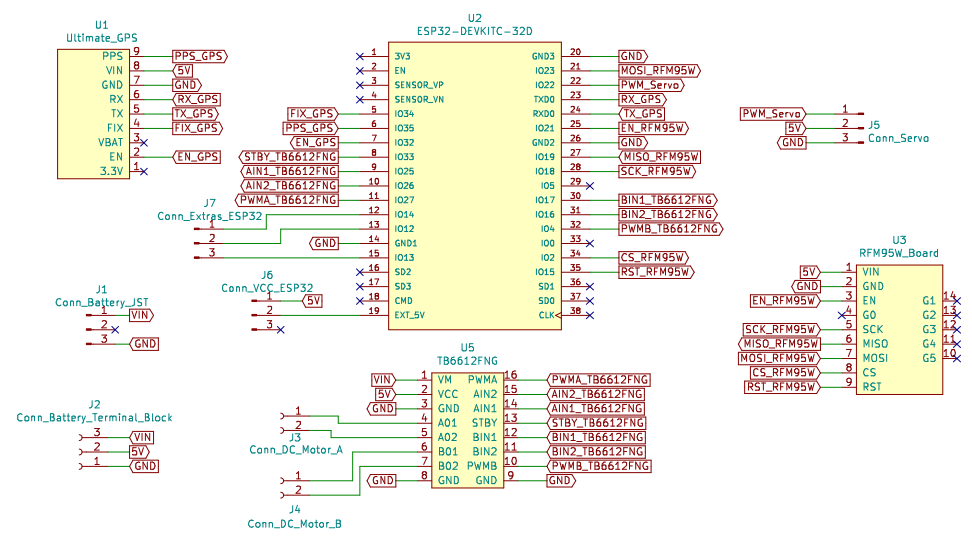
Schematic of Buoy B v1.0.
For more information about the design check the original post in the project's page.
Layout
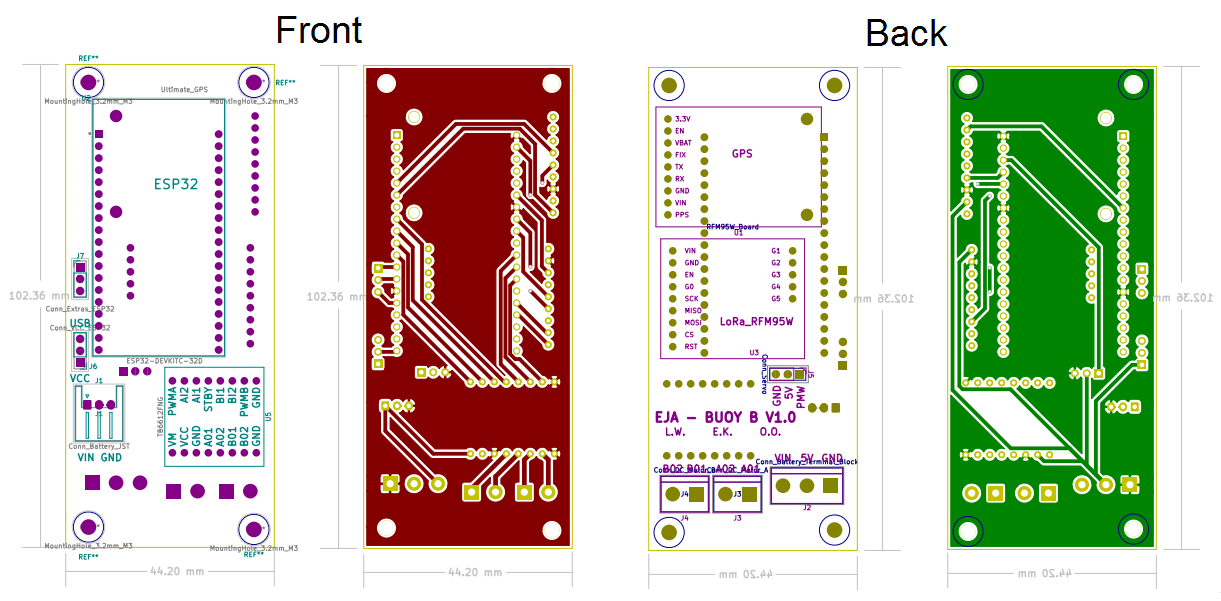
PCB Layout of Buoy B v1.0.
PCB
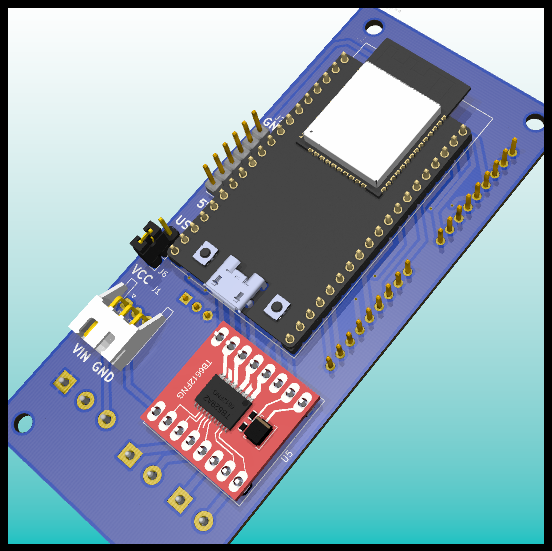
PCB: Front Layer with components.
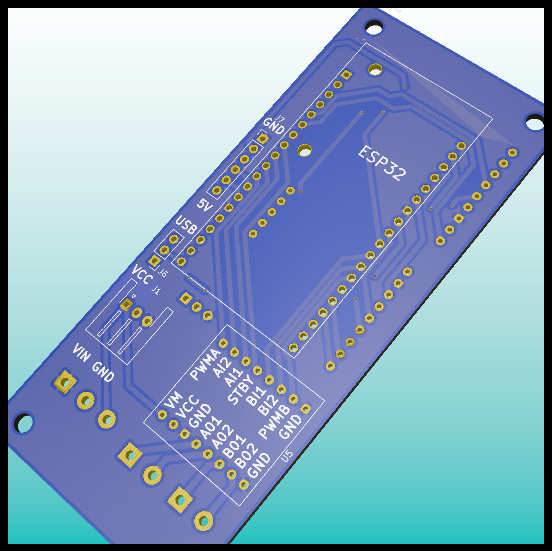
PCB: Front Layer without components.
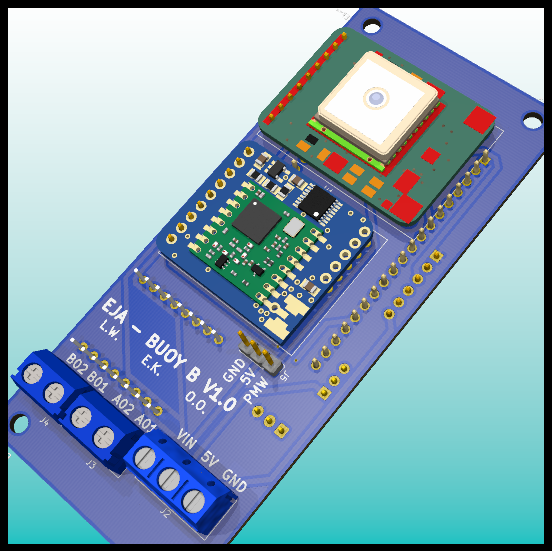
PCB: Back Layer with components.
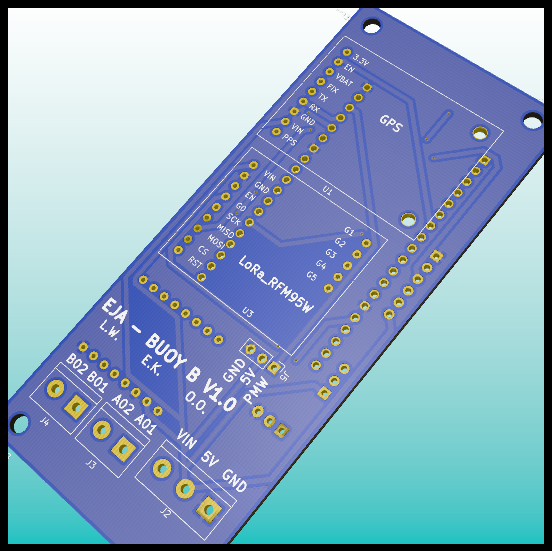
PCB: Back Layer without components.
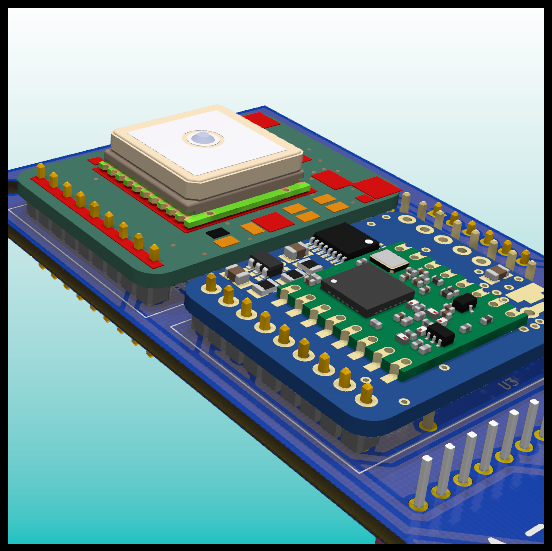
PCB: GPS and LoRa Module.
PCB: Motor Driver.
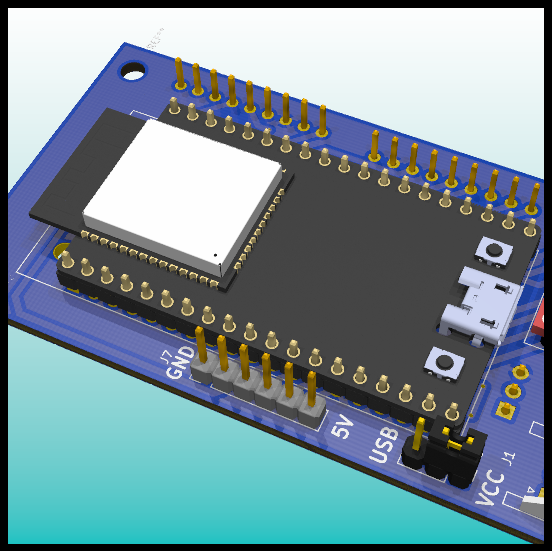
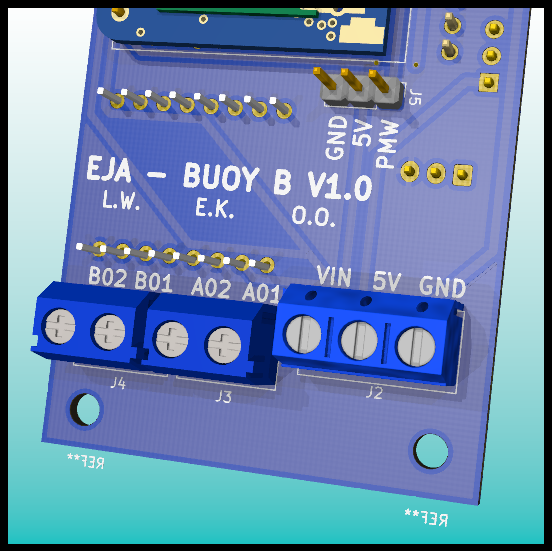
PCB Design: ESP32 and Connectors.
Assembly
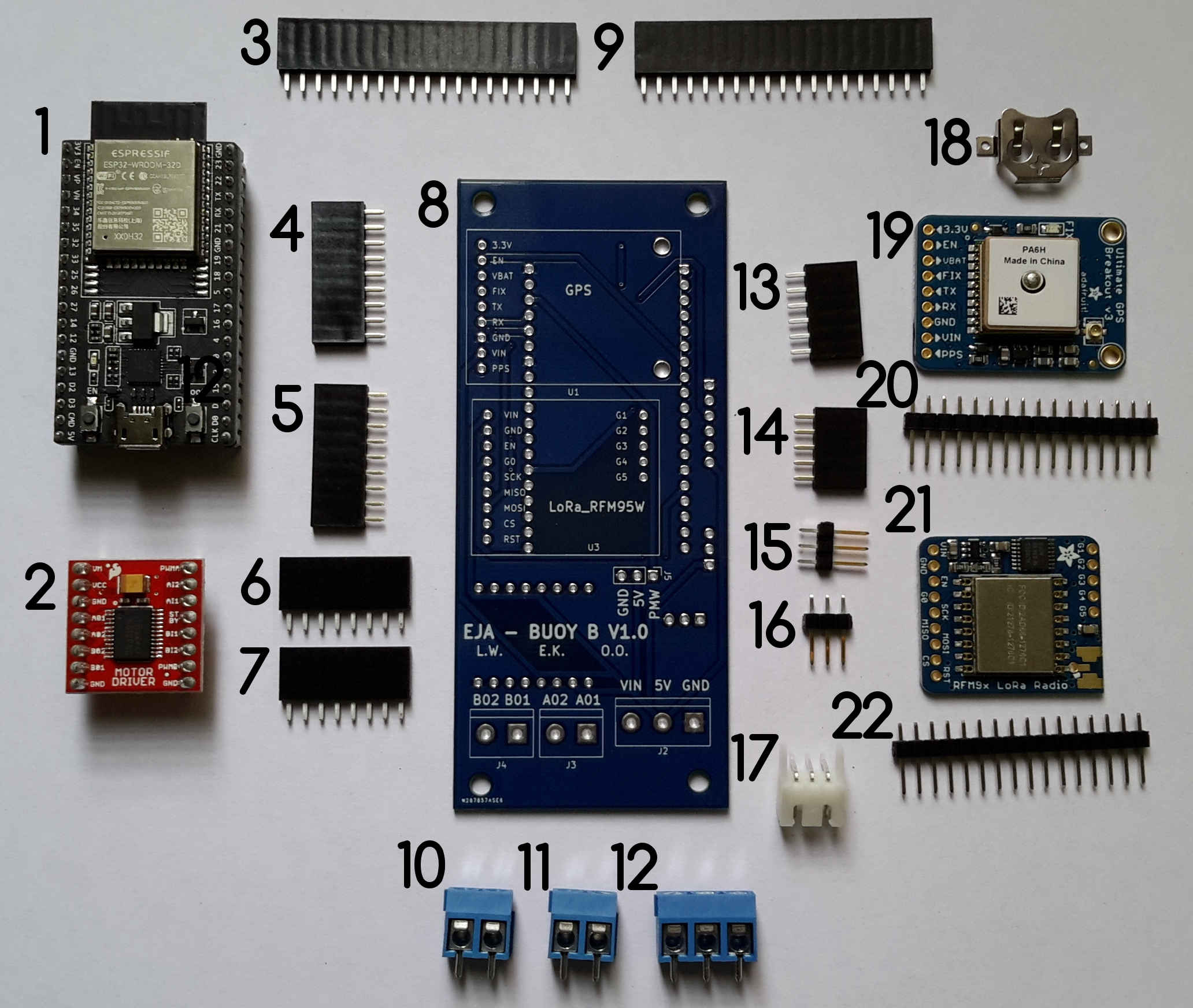
Components of Buoy B v1.0.
Components List:
- ESP32-DEVKITC-32D
- TB6612FNG MOTOR DRIVER BOARD
- CONN HDR 19POS 0.1 TIN PCB
- CONN HDR 9POS 0.1 GOLD PCB
- CONN HDR 9POS 0.1 GOLD PCB
- CONN HDR 8POS 0.1 TIN PCB
- CONN HDR 8POS 0.1 TIN PCB
- PCB Buoy B V1.0
- CONN HDR 19POS 0.1 TIN PCB
- TERM BLK 2P SIDE ENT 5.08MM PCB
- TERM BLK 2P SIDE ENT 5.08MM PCB
- TERM BLK 3P SIDE ENT 5.08MM PCB
- CONN HDR 6POS 0.1 TIN PCB
- CONN HDR 5POS 0.1 GOLD PCB
- CONN HEADER VERT 3POS 2.54MM
- CONN HEADER VERT 3POS 2.54MM
- CONN HEADER R/A 3POS 2.5MM
- Coin cell holder (included in Adafruit Ultimate GPS)
- Adafruit Ultimate GPS
- CONN HDR 16POS 0.1 TIN PCB (included in Adafruit Ultimate GPS)
- RFM95W LoRa Radio
- CONN HEADER VERT 16POS 2.54MM (included in RFM95W LoRa Radio)
For a detailed Bill of Materials visit the following post.
For a detailed explanation about the soldering and assembly procedure visit the following post.
Wiring Diagrams
The original design of the board considered the following components:
Power Management
- Battery (5V < Voltage < 15V)
- PCB Board Buoy B V1.0
- Buck Converter
- Switch
- Extra capacitor
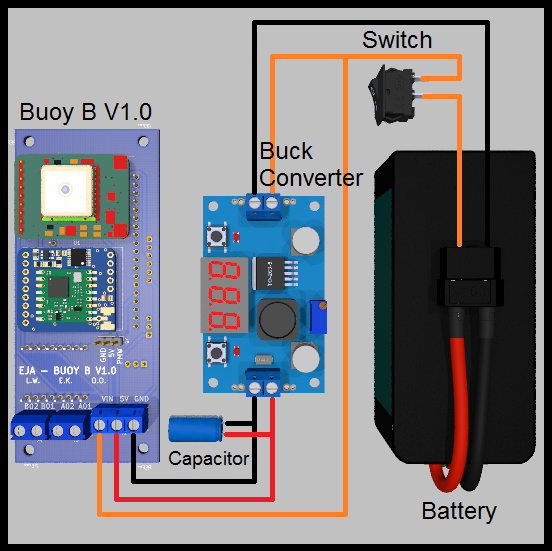
Wiring diagram: Power Management with Buck Converter.
Also, there is an alternative for the battery management, is possible to provide the required voltages with a boost converter and a 3.7V Battery, like the following example:
- 3.7V 1 Cell Battery
- PCB Board Buoy B V1.0
- Boost Converter
- Micro USB Breakout Board
- Switch
- Extra capacitor
- JST-XH 2 Pos female connector and a JST-XH 2 Pos male connector
- 5V Charger (only used to charge the battery)
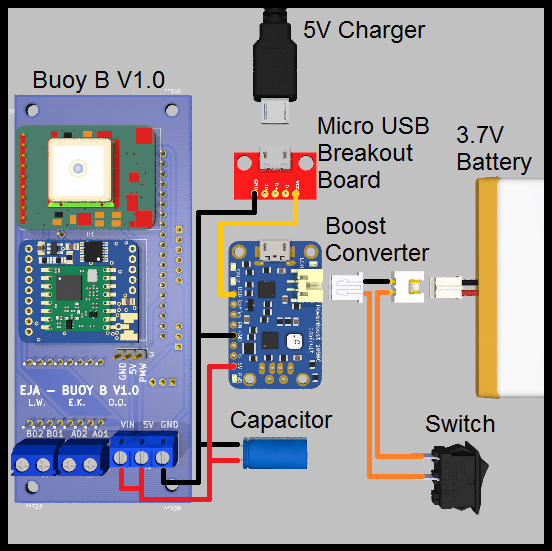
Wiring diagram: Power Management with Boost Converter.
This alternative is valid and possible, but is not ideal for longer working time (compared to the first one). It is important to consider the efficiency of the boost converter. The selected boost converter will have a voltage drop at a current higher than 500mA, that should be taken into consideration.
Motors
The board was designed to handle 3 different types of motors, those are:
- Servo Motor
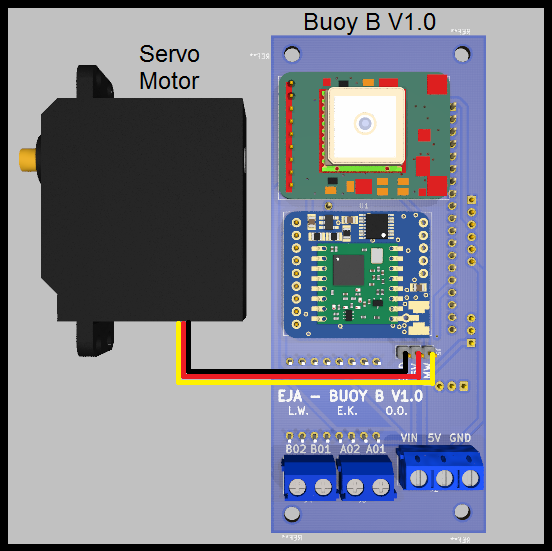
Wiring diagram: Buoy B v1.0 with Servo Motor.
- Stepper Motor (using the driver TB6612FNG)
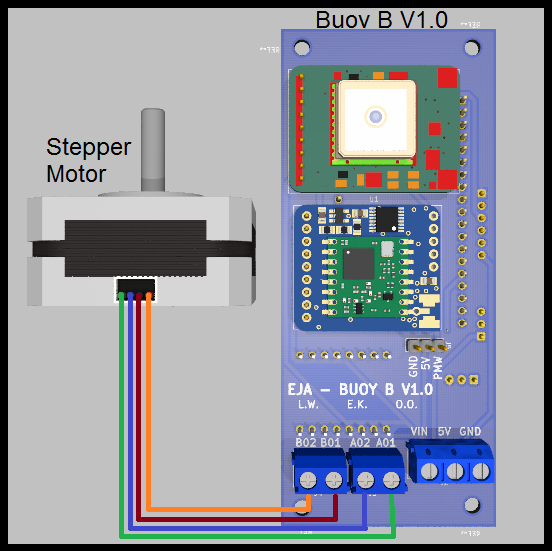
Wiring diagram: Buoy B v1.0 with Stepper Motor.
- DC Motor (using the driver TB6612FNG)
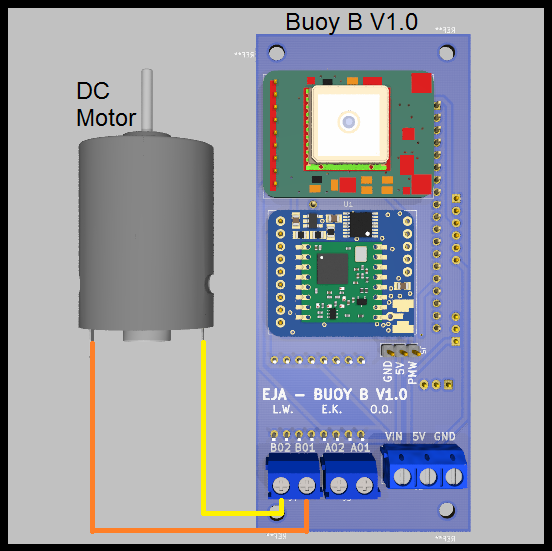
Wiring diagram: Buoy B v1.0 with DC Motor, first connector.
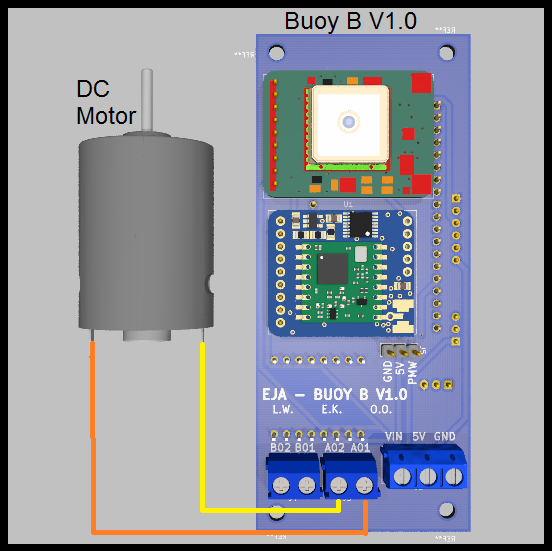
Wiring diagram: Buoy B v1.0 with DC Motor, second connector.
For more information about the wiring diagrams and the project visit the following post.
User Interface
Requirements:
- ESP32 Add-on in Arduino IDE
- ESPAsyncWebServer
- AsyncTCP
- SPIFFS File System
- ESP32 Async Over The Air
- TinyGPSPlus
- LoRa
The ESP32 creates an Asynchronous Web Server, with the following credentials:
const char* ssid = "EJA_Buoy_B";
const char* password = "123456789";
With those credentials it is possible to access the WiFi network.

The ESP32 creates a Domain Name System (DNS) to assign a domain name to the web server. That means that it is not necessary to know the server IP, it is possible to access the web server using the defined domain name for the host, in this case, the name is:
const char* host = "www.buoy_b.eja";
Once the device (phone/computer) is connected to the server (EJA_Buoy_B), open a browser and visit the following url:
http://www.buoy_b.eja/
Home
The previous link displays the web page used for HOME:
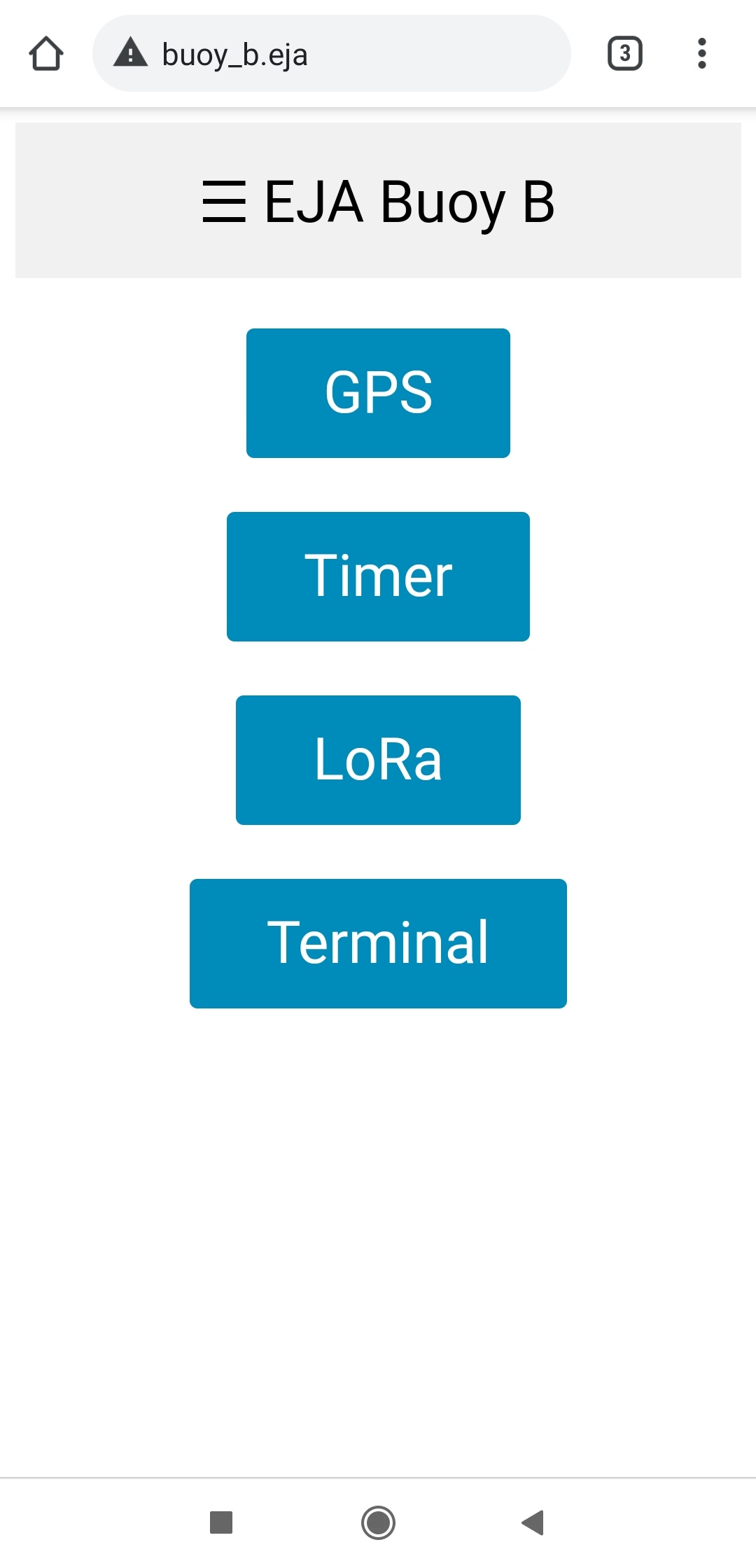
There is a header with the name "EJA Buoy B" that opens a sidebar with links to the different test functionalities. It is also possible to access those pages using the buttons in HOME.

GPS
The page http://www.buoy_b.eja/gps shows the data from the GPS module.

Timer
The page http://www.buoy_b.eja/timer shows the interface to create a timer in the Buoy. The timer represents a countdown that activates the release mechanism when the time has reached zero. The initial page allows the user to set the timer.
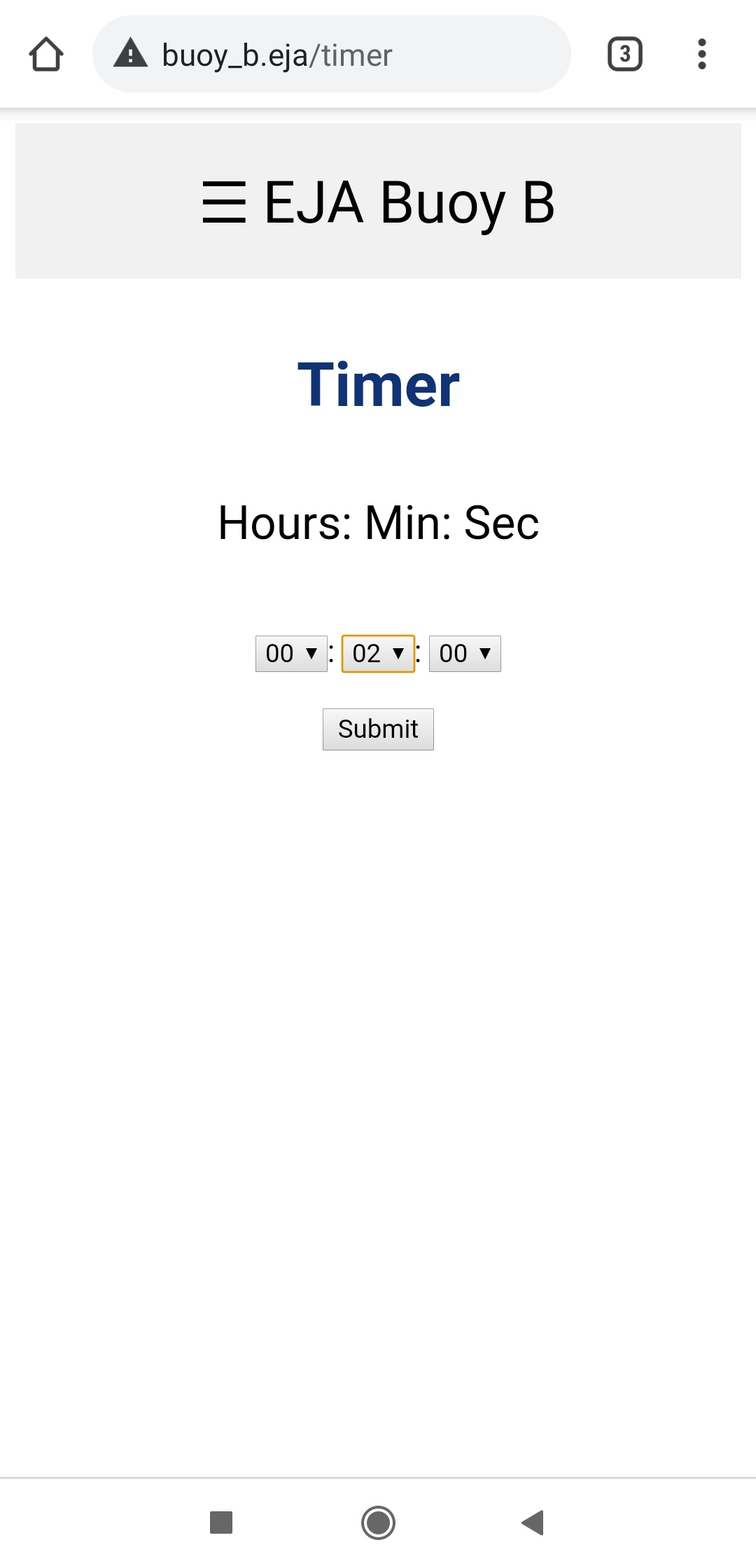
After selecting the amount of time the user has to click the Submit button. That will create the timer, the interface displays the countdown to the user.
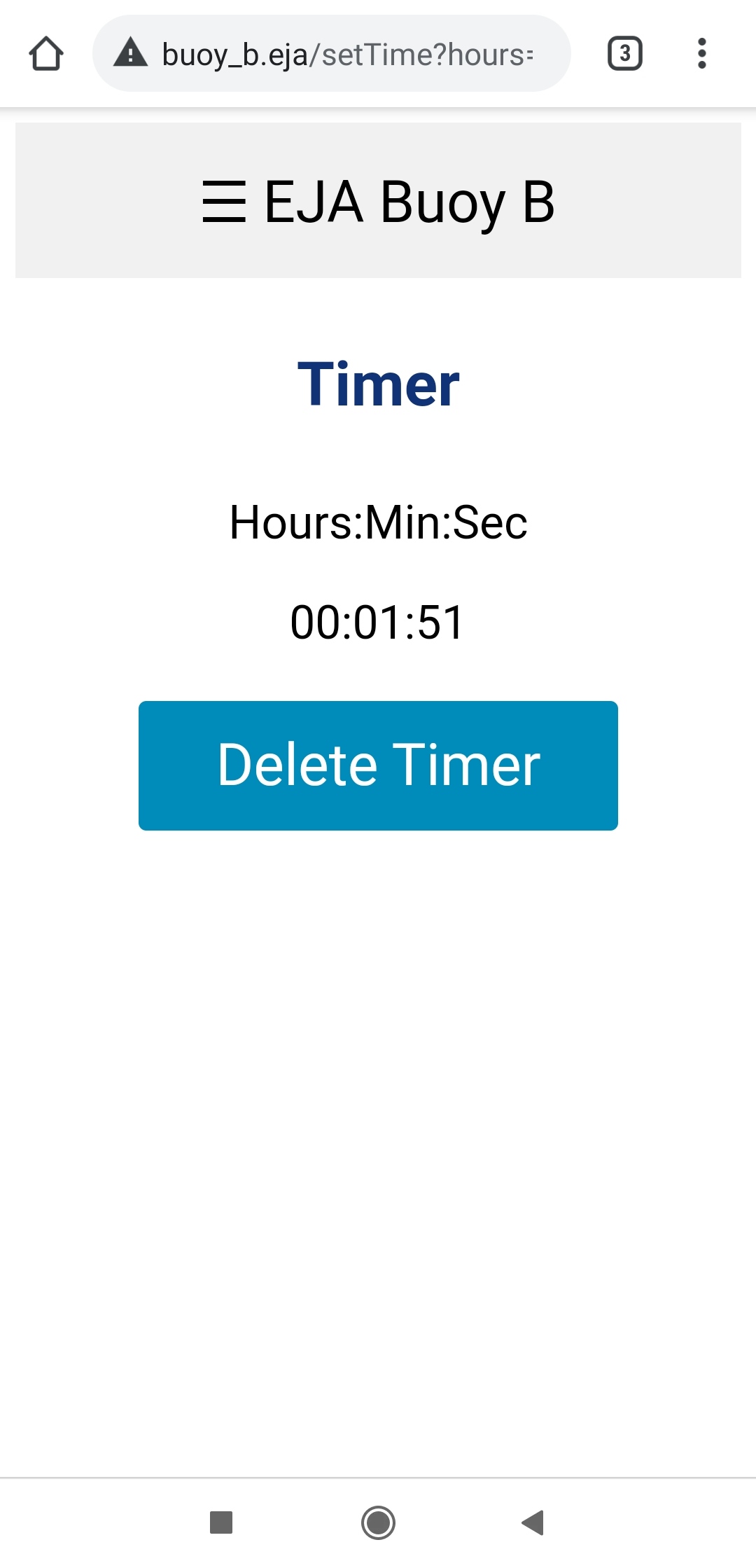
When the timer reaches zero, the Buoy activates the release mechanism.
The user can delete the timer at any time clicking the button Delete Timer. When the user deletes the timer, it is possible to create a new one a restart the process.
LoRa
The page http://www.buoy_b.eja/lora shows internal messages related to LoRa. In the ESP32 that information is stored in the variable:
String lora_all_msg = "";

Terminal
The page "http://www.buoy_b.eja/terminal" shows internal messages. In the ESP32 that information is stored in the variable:
String terminal_messages = "";

Future Improvements
For more information about the recommended future improvements for the electronic design visit the following post.